CT SCAN BASIC
CT SCAN INDICATION
A CT scan is used for numerous clinical indications depending on the organs to evaluate.The CT scan can be utilized in both inpatient and outpatient clinical settings. In an emergent setting, it can rule out serious illness. Indications for obtaining a CT scan are to help the physician diagnose, narrow the differential diagnosis, and confirm the doctor's suspicions. It can also be used for cancer screening, staging, and follow-up. Its use helps to perform biopsies adequately and to assist during a surgical procedure.
- Brain: tumors, traumatic or spontaneous hematomas, stroke, edema, skull fracture, calcifications, arteriovenous malformations, hydrocephalus, sinusitis, and empyema
- Neck: tumors, benign masses, thyroid nodules, lymphadenopathy
- Chest: tumor, pneumonia, metastasis, benign masses, pulmonary edema, pleural edema, tuberculosis, pulmonary embolism, traumatic injury to the lungs, esophageal rupture, ingested foreign body, fibrosis
- Abdomen: primary tumors, metastases, abscess, ascites, cholecystitis, appendicitis, renal calculi, pancreatitis, obstruction, lymphadenopathy, foreign body
- Spine: fractures, degenerative changes, stability, osteomyelitis, disc pathology
- Bone: complex bone fractures, eroded joints, knee, tumors, osteomyelitis
- Gyn: cyst, fibromas, tumors
- Screening: colon and lung cancer. CT colonography/colonoscopy is used to diagnose colon disease and early-stage cancer with good sensitivity and specificity. Low-emission CT can be used to diagnose lung cancer in smokers and former smokers with a high smoking history aged between 55 and 80 years old using a low radiation dose.
- Biopsy: CT guided to different organs for adequate tissue extraction
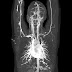
- CT Angiography: brain, heart, lung, kidney, extremities
- Intraoperative: CT scan can be used for neuronavigation procedures during brain biopsy or tumor resection.








0 Comments