ANGIOGRAM BASIC
PREPATION
- Serum Creatinine.
- Empty Stomach.
- Tray.
- Injection Phenergan / Hydrocortisone.
- Apply 18G Cannula to Right Hand.
- Old Documents.
- Neck / Cerebral ------------------ Arch of Aorta.
- Coronary Artery ----------------- Descending Aorta.
- Pulmonary------------------------- Pulmonary Trunk.
- Renal / Abdominal Artery -------Renal / Abdominal Aorta (First Slice).
- Upper Limb ---------------------- Arch of Aorta.
- Lower Limb ----------------------Abdominal Artery / Arch of Aorta (if need arch of aorta).
- Neck / Cerebral-----------------50 ml--------------05 ml/sec.
- Coronary Artery---------------- 60-70 ml----------05 ml/sec.
- Pulmonary-----------------------50-60 ml--------- 05 ml/sec.
- Renal / Abdominal Artery ---- 80-100 ml--------05 ml/sec.
- Upper Limb -------------------- 100 ml------------05 ml/sec.
- Lower Limb -------------------- 120-130 ml-------05 ml/sec.
IV CANULA SIZES FLOW RATES
- DEEP GREEN------------18G--------- 5-7 ml/sec-----------------76 ml/min
- PINK-----------------------20G--------- 3.5-4.5 ml/sec------------54 ml/min
- DEEP BLUE--------------22G--------- 2.5-3.5 ml/sec------------31 ml/min
CT ANGIOGRAPHY INDICATION
- Aneurysms.
- Blockages.
- Blood clots.
- Congenital (birth-related) abnormalities of the cardiovascular system, including the heart.
- Disorganized blood vessels, such as vascular malformations.
- Injury.
- Tumors.
- Vessel rupture or tears.
INDICATION FOLLOWING SURGERY
- Identify abnormalities, such as aneurysms, in the aorta, both in the chest and abdomen, or in other arteries.
- Detect atherosclerotic (plaque) disease in the carotid artery of the neck, which may limit blood flow to the brain and cause a stroke.
- Identify a arteriovenous malformation inside the brain or elsewhere.
- Detect plaque disease that has narrowed the arteries to the legs and help prepare for angioplasty/stent placement or surgery.
- Detect disease in the arteries to the kidneys or visualize blood flow to help prepare for a kidney transplant or stent placement.
- Guide interventional radiologists and surgeons making repairs to diseased blood vessels, such as implanting stents or evaluating a stent after implantation.
- Detect injury to one or more arteries in the neck, chest, abdomen, pelvis, or limbs following trauma.
- Evaluate arteries feeding a tumor prior to surgery or other procedures such as chemoembolization or selective internal radiation therapy.
- Identify dissection or splitting in the aorta in the chest or abdomen or its major branches.
- Show the extent and severity of coronary artery disease and its effects and plan for an intervention, such as a coronary bypass and stenting.
- Examine pulmonary arteries in the lungs to detect pulmonary embolism (blood clots, such as those traveling from leg veins) or pulmonary arteriovenous malformations.
- Look at congenital abnormalities in blood vessels, especially arteries in children (e.g., malformations in the heart or other blood vessels due to congenital heart disease).
- Evaluate stenosis and obstructions of vessels.
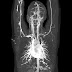
CT ANGIOGRAPHY
- Brain/Cerebral.
- Neck/carotid.
- Coronary Artery.
- Pulmonary artery
- Abdominal aorta
- Renal Artery.
- Pelvis.
- Legs and feet.
- Arms and hands.
CONTRAINDICATION
- Previous severe reactions to iodinated contrast media
- Non-compliance








0 Comments